Biomolecular Electronics
Engineering Charge-Transport in Bioelectronic Devices
Bioelectronics is an emerging field that has captivated widespread interest over the past decade. From unraveling how charge is transferred inside cells during processes like respiration to designing nanoscale electronic platforms for in vivo measurements, this young research field holds formidable potential.
Nanoscale electronics require interfacing complex biomolecular moieties (e.g. proteins) with electronic platforms for signal transduction. This necessitates a bottom-up understanding of how the electrical signatures of a biomolecular circuit relate to the properties of the sensing moiety (e.g., structure, dynamics).
The rather complex nature of this phenomena called for interdisciplinary approach combining large-scale protein dynamics mimicking STM-induced manipulations (via dedicated MD simulations), a detailed understanding of electronic properties (collaboration with Dr. Linda Zotti), advanced single-molecule experiments (group of Prof. Ismael Díez-Pérez), and biomolecular engineering (Prof. Pau Gorostiza).
Our works have unraveled a wide range of surprising results, to name a few:
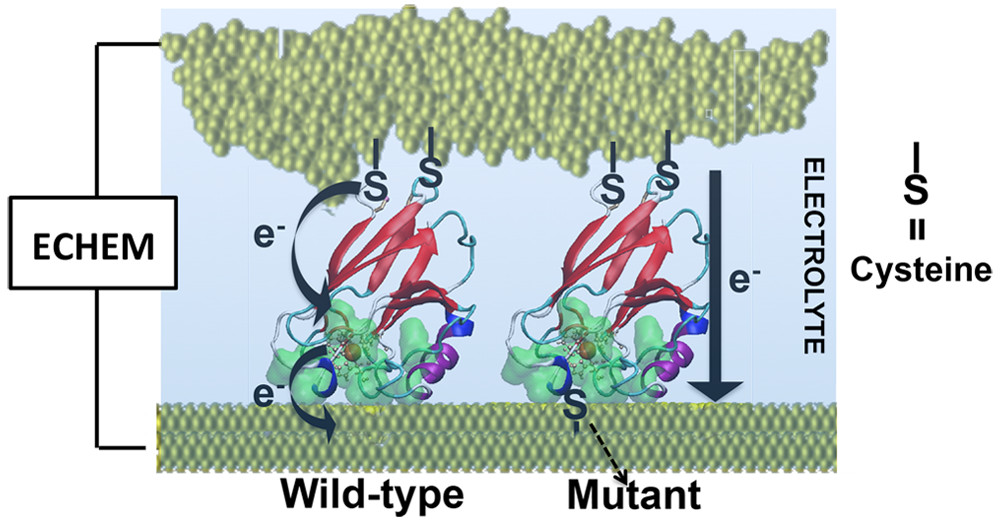
Demonstrating that charge transport in single-protein junctions can be finely regulated via single-point mutations, altering just 1% of the atoms.
Showing that single-point mutations can block vibration modes crucial for charge transport, effectively switching the two-step tunneling process on and off.
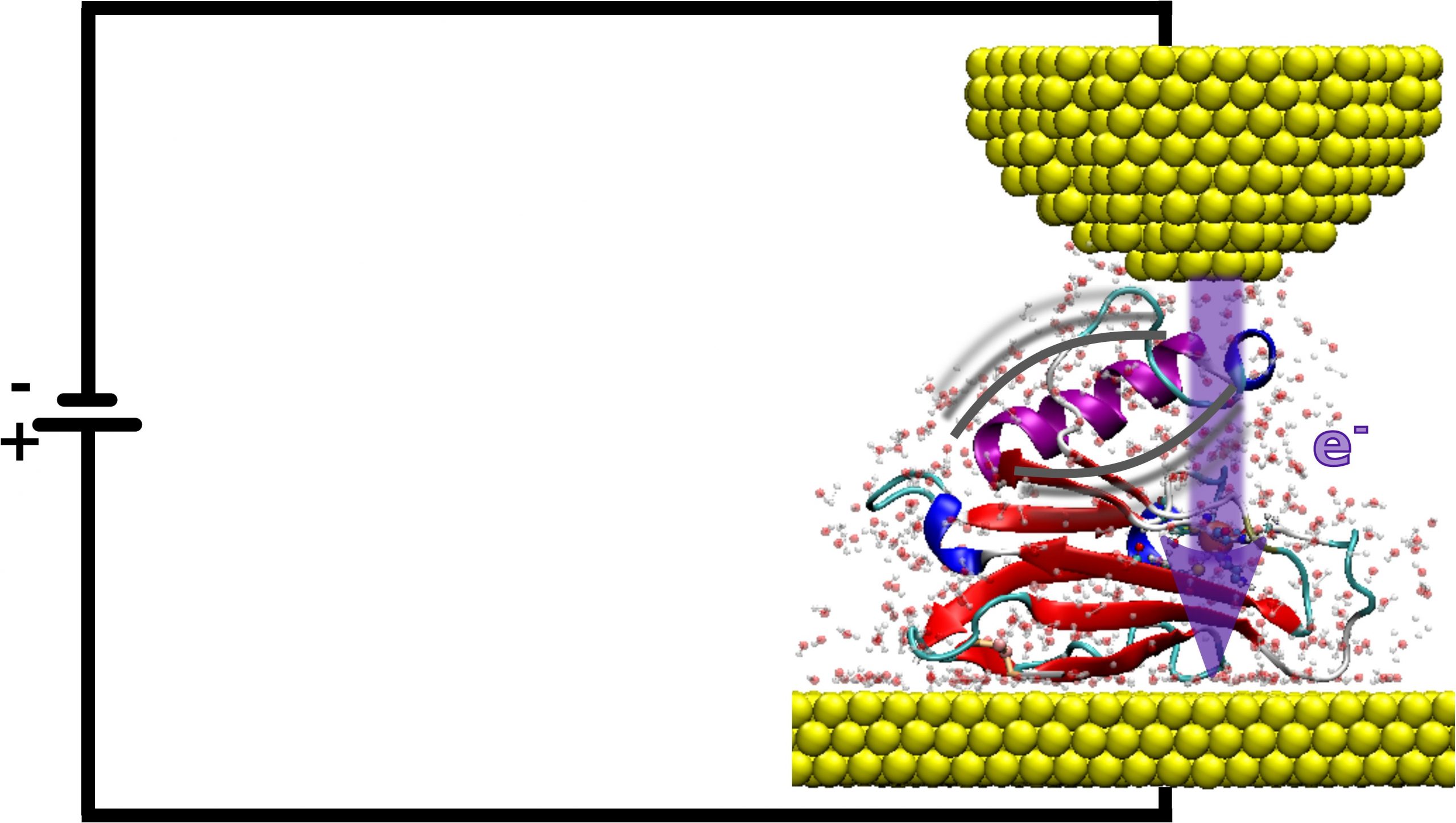
Revealing that conductance in nanometer-sized proteins can match that in much shorter molecular contacts by identifying new mechanisms involving surrounding waters and protein deformation.
Publications
C. Roldán, C. Romero, I. Díez, J. G. Vilhena, R. Pérez, J. C. Cuevas, and L. A. Zotti. “Efficient Electron Hopping Transport through Azurin-Based Junctions”. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 14 (49), 11242 (2023) — featured in The Front Cover
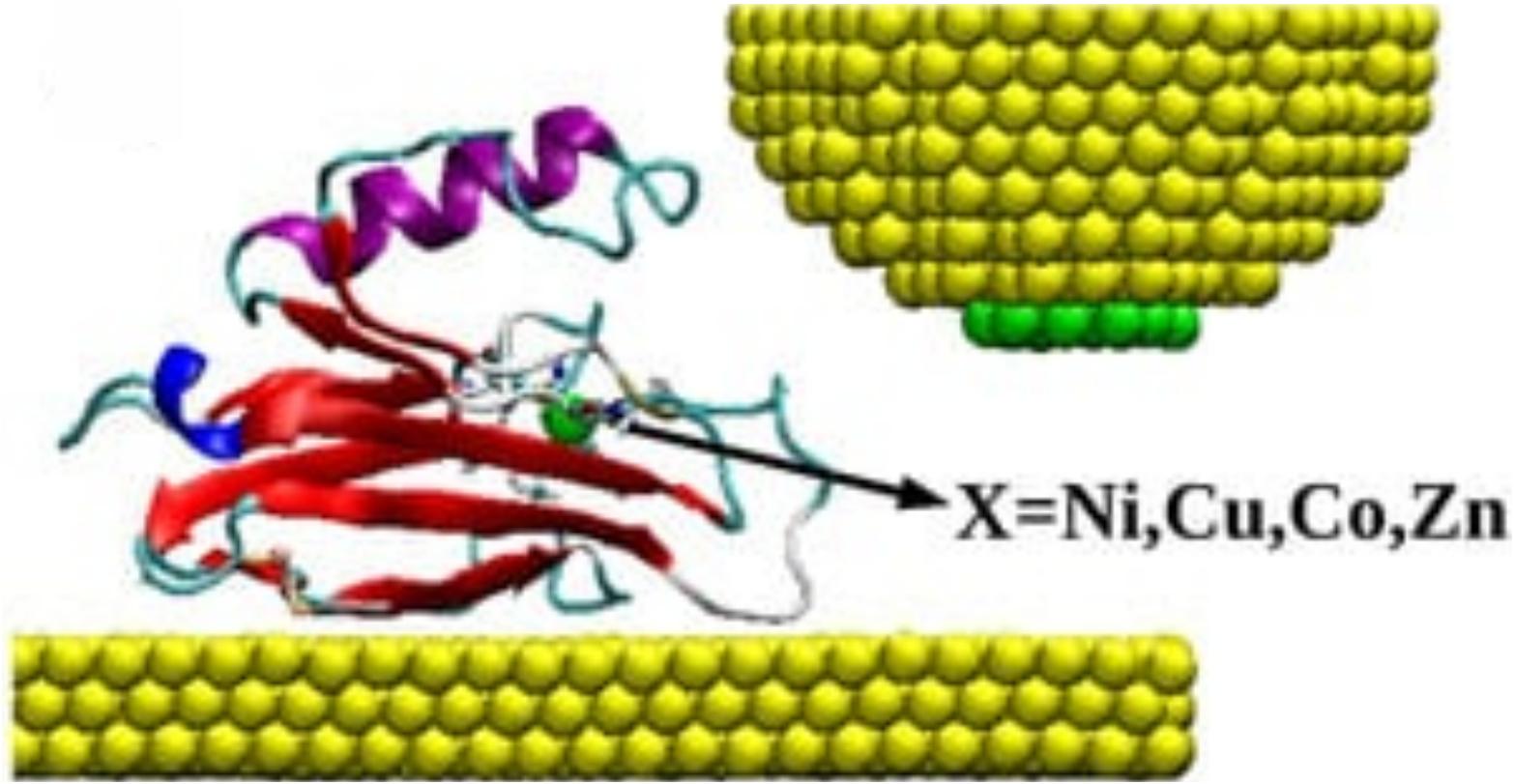
C. Romero, M. Ortega, J. G. Vilhena, R. Pérez, J. C. Cuevas and L. A Zotti. “The Role of Metal Ions in the Electron Transport through Azurin-Based Junctions“. Applied Sciences 11, 3732 (2021).
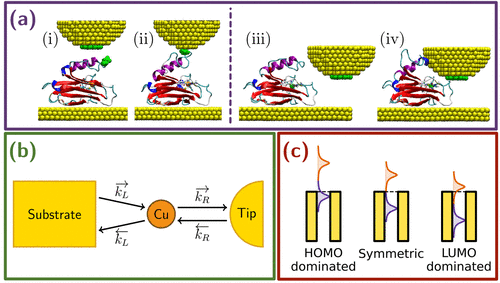
C. Romero, M. Ortega, J. G. Vilhena, I.Díez, R. Pérez, J. C. Cuevas and L. A. Zotti. “Can Electron Transport through a Blue-Copper Azurin Be Coherent? An Ab-Initio Study“. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 125(3), 1693 (2021).
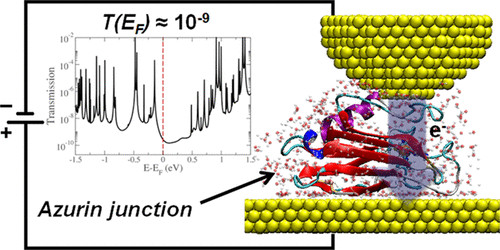
M. Ortega, J. G. Vilhena, L. A. Zotti, I. Díez, J. C. Cuevas and R. Pérez. “Tuning Structure and Dynamics of Blue Copper Azurin Junctions via Single Amino-Acid Mutations“. Biomolecules 9, 611 (2019).
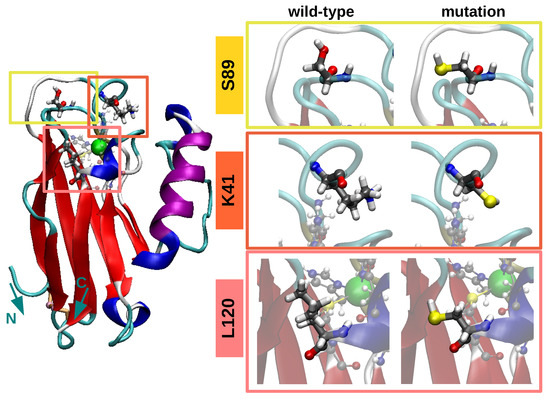
C. Romero, M. Ortega, J. G. Vilhena, I. Diéz, J. C. Cuevas, R. Pérez and L. A. Zotti. “Mechanical Deformation and Electronic Structure of a Blue Copper Azurin in a Solid-State Junction“. Biomolecules 9, 506 (2019).
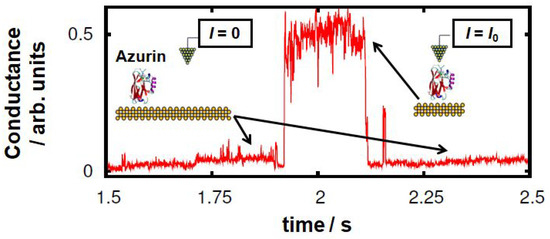
C. Romero, M. Ortega, J. G. Vilhena, I. Díez, J. C. Cuevas, R. Pérez and L. A. Zotti. “Ab-initio Electronic Structure Calculations of Entire Blue Copper Azurins“. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 20, 30392 (2018).
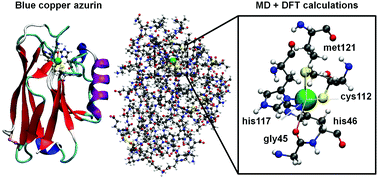
M. P. Ruiz, A. C. Aragonès, N. Camarero, J. G. Vilhena, M. Ortega, L. A. Zotti, R. Peréz, J. C. Cuevas, P. Gorostiza and I. Díez. “Bioengineering a Single-Protein Junction“. Journal of the American Chemical Society 139 (43), 15337 (2017).